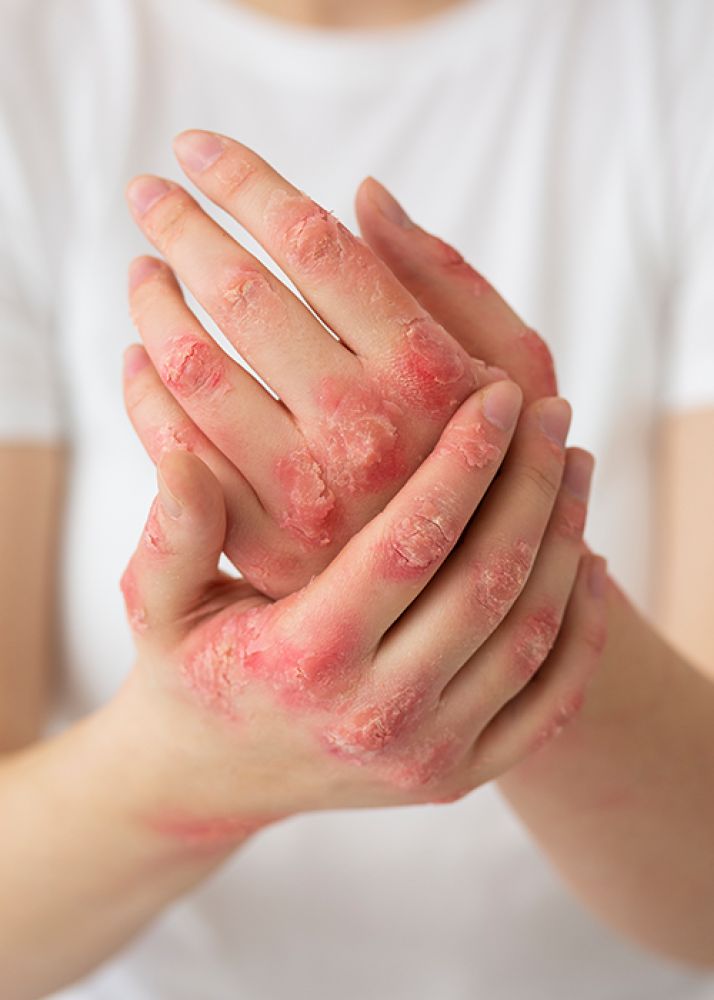
HPV and Its Effects on the Skin: Prevention and Treatment
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common virus that can cause various lesions on the skin and mucous membranes. While HPV is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, some types can also spread through direct skin contact. Certain types of this virus lead to warts, lesions, and other effects on the skin, while others may cause more serious health issues. Understanding HPV’s impact on the skin and learning prevention methods are essential for maintaining our health.
HPV, short for human papillomavirus, is a group of highly prevalent viruses that cause infections on the skin and mucous membranes. There are over 100 types of HPV, each of which can affect different areas of the skin or mucosa. Some types cause common skin warts, while others lead to wart formations in the genital area. Certain high-risk HPV types may even cause cellular changes that can lead to cancer.
The most common effect of HPV on the skin is the formation of warts. The virus settles in the upper layers of the skin, causing abnormal cell growth that appears as wart-like lesions. The primary effects of HPV on the skin include:
Most HPV effects on the skin are harmless and primarily cause cosmetic concerns. However, some high-risk HPV types, if untreated or neglected, can lead to cellular changes that may result in cancer. High-risk genital HPV infections, for example, can increase the risk of cervical cancer in women and penile cancer in men.
Preventing HPV is vital for skin health. To avoid HPV infections and prevent its spread, consider the following preventive measures:
HPV infection treatment focuses on eliminating skin lesions and preventing the virus from spreading. While HPV cannot be entirely cured, various treatments can alleviate its effects on the skin:
HPV’s effects on the skin can vary from person to person and may pose health risks in some cases. If you notice warts, lesions, or HPV-related symptoms on your skin, consulting a dermatologist is essential. Your dermatologist can determine the most appropriate treatment options to manage HPV infections and alleviate its effects on your skin, helping you maintain your health.
Remember, regular doctor visits and adherence to hygiene practices are crucial to managing HPV and protecting your skin health.
Winter Skin Care

Daily Skincare Routine

Anti-Aging Skincare: What to Pay Attention to?
Ways to Manage Eczema

HPV and Its Effects on the Skin

You can easily reach us through our contact page. Please fill out the form for your questions, suggestions or appointment requests.
Address
Hançerli Mah. Fatih Sultan Mehmet Cad. No: 155 İlkadım/SAMSUN
Show on GoogleMapinfo@gulsekerlisoytatar.com.tr
Working Hours
Monday-Saturday
09:00 - 17:00